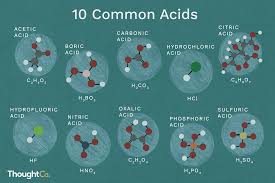
Boric acid (H3BO3), an acid since it dissociates according to the balance and has been proved by Biswanger with massive doses, but its acts are only known from accidental toxicity. There are some known boric acids that are derived from boron trioxide with differing quantities of oxygen. The most important of these is ortho boric acid, or boric acid. As demand for boric acid arose due to the enormous borax use in the porcelain fabrication. When obtained from these sources, boric acid crystals contain ammonia salts, among other impurities.
Phosphorus contains organic fertilizers, phosphoric acid, which is commonly used worldwide as phosphate salts which derivatives. Many phosphoric acid compounds, except fertilizer products, are derived from ortho phosphoric acid, formed by oxidation of elemental phosphorus. In addition to their very significant use in fertilizers, phosphorus derivatives are extensively used in food and medicine as well as water treatment, plasticizing in the plastic and lacquer industries, flameproofing of fabric and paper, petroleum processing, rustproofing of metal and for a vast variety of miscellaneous uses.
Properties of Boric Acid
Boric acid also known as boracic acid, hydrogen borate, ortho-boric acid and acid boricum is a solid, monobasic boron Lewis acid sometimes used as an insecticide, antiseptic, neutron absorber or precursor to other chemical compounds. This has the molecular formula H3BO3 and is dissolved in water in the shape of colourless crystals or a white powder.
Boric acid or H3BO3 chemical formula Boric Powder is the final result of boron halide and hydride hydrolysis. Boric powder is commonly obtained in chemical processes by acidifying and heating borax solution. Boric acid is a glossy white crystal form comprising B(OH)3 connected in infinite layers of hexagonal symmetry by hydrogen bonding, and mildly soluble in water solution. Boric acid is a weak acid property of pH is 9.2, and is not used as a donor to hydrogen ions but as a lewis acid with the hydroxyl ion taking the electron pair.
Applications of Phosphoric Acid
Another of the most commonly known and used acids in farming, chemical and medical applications is phosphoric acid, also known as orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4). This is used as an ingredient for acidifying foods and drinks like various colas, offering a flavor that is tangy or bitter.
Different applications of phosphoric acid include:
- Phosphoric acid is also used for metal etching and tooth enamel roughing during dental procedures such as root canals and whitening of the dentures.
- Phosphoric acid solutions are produced for use in rust treatment as a dipping bath or spray and can be added to rusted areas.
- Some phosphoric acid is used in fertilizer processing, where the acid is added to the minerals present in phosphate rock to create phosphate salts.
- Certain applications include pharmaceuticals, products for washing, and as chemical reagent.
Phosphoric acid is a white, non-volatile, odourless oil. When condensed it’s mildly viscous with a syrupy consistency. This is usually available for various industrial and experimental uses in 85 percent concentration and in more distilled solutions.








Be the first to write a comment.